Governance - Risk - Compliance Management (GRC)
Approaches for implementation in the QM-Pilot
Governance, risk management and compliance summarises the three most important levels of action for the successful management of a company. The following is an example of how this can be implemented for G-R-C in the QM-Pilot.
Governance - managing internal guidelines
Mapping of business processes in the Process Management module (see product information brochure) including data from the Document Management and Risk Management modules. This enables a holistically structured management system. In addition to mapping the process map, detailed process descriptions as flow charts or BPMN swimlanes can be enriched with company-specific data. The data fields are flexibly configurable and can cover the following points, among others, and can be extended as required:
- Targets (at each process level, detailed targets or cross-company targets)
- Implementation methodology (derived from the processes and related information)
- Indication of the necessary resources for a process - Reporting for overall evaluation
In addition, all (internal) specification documents are managed, versioned, archived and always made available in the document module (see product information) and can be set in connection with processes, risks and compliance requirements.
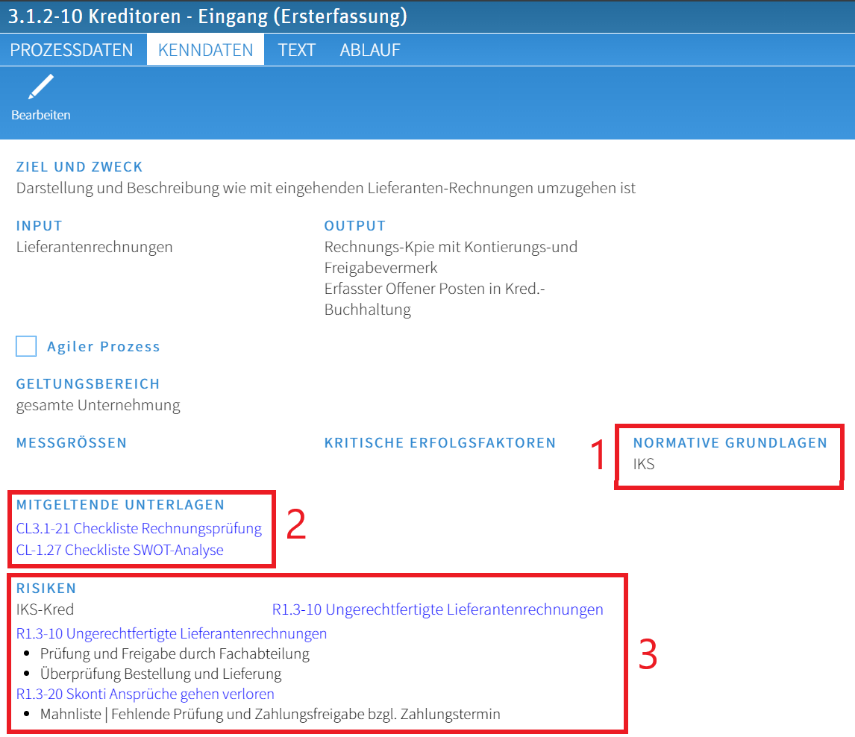
- Documents can be linked directly to process steps or in the characteristic data (2) and are always available only in the currently released version
- Documents/processes can be linked to risks (3)
- Normative foundations can be linked to documents (1)
- All connections/dependencies can be displayed/traced
Example Characteristic data acquisition for the process including links to documents and risks:
Riskmanagement
Risk management is a management task in which the risks of an organisation are identified, analysed and evaluated. For a holistic approach, it is important that risk management does not stand alone, but is linked to governance and compliance in the overall business framework.
Risk recording (risk data, description, measures/controls, risk matrix)
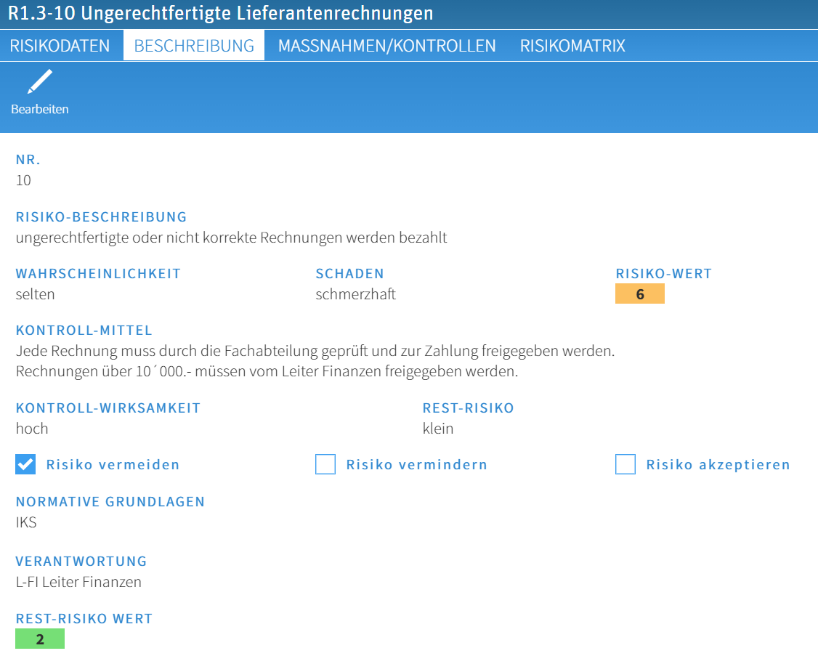
The fields shown can be configured according to customer requirements. Data such as the risk description, evaluation, risk appetite, normative principles and responsibilities are easy to record and evaluate via reporting. Calculated risk values can be displayed on the risk matrix. All dependencies to other system contents (e.g. process steps in the ICS) can be evaluated.
Evaluation schemes can be stored in master data tables and made available in the risk description via selection lists. It is also possible to evaluate which criteria are specified in which risks.
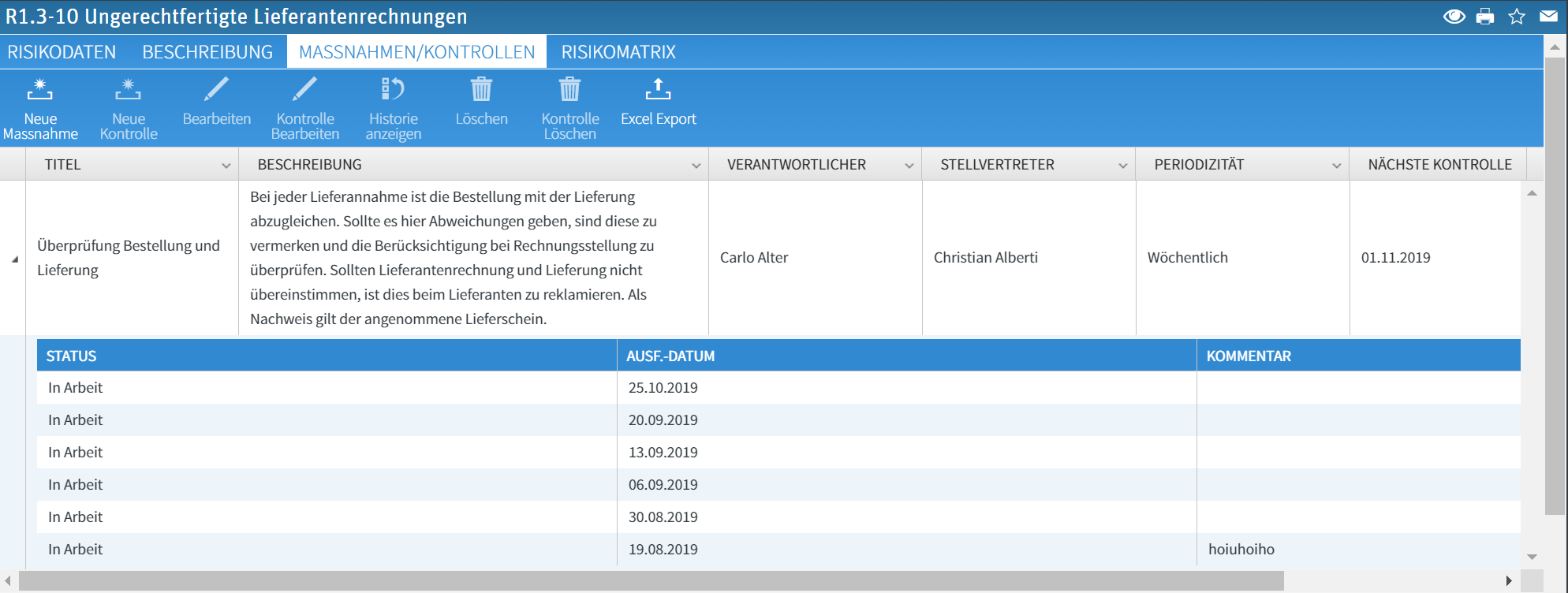
For each risk, any number of measures can be recorded and the corresponding controls can be created automatically by the system. Responsibility and deputy can be clearly assigned here. For documentation in the system, the controls are documented by the users with a status (in progress, completed, rejected, completed with defect) and stored in the history:
Reporting
In addition to a large number of standard reports (risk list, risks with description, list of measures, controls, ICS risk control matrix, etc.), specific reports can be requested and stored by Abel Systems for special reporting requirements.
Compliance
Compliance Management describes the principles and measures for adhering to laws, guidelines and internal codes as well as for avoiding violations of rules.
The entirety of these laws, standards, guidelines as well as internal and external specifications must first be recorded as an overview in a GRC system. This is done via a master data table, which can be supplemented with additional information (scope of application, links to documents, etc.).
Example master data table standards/laws/guidelines
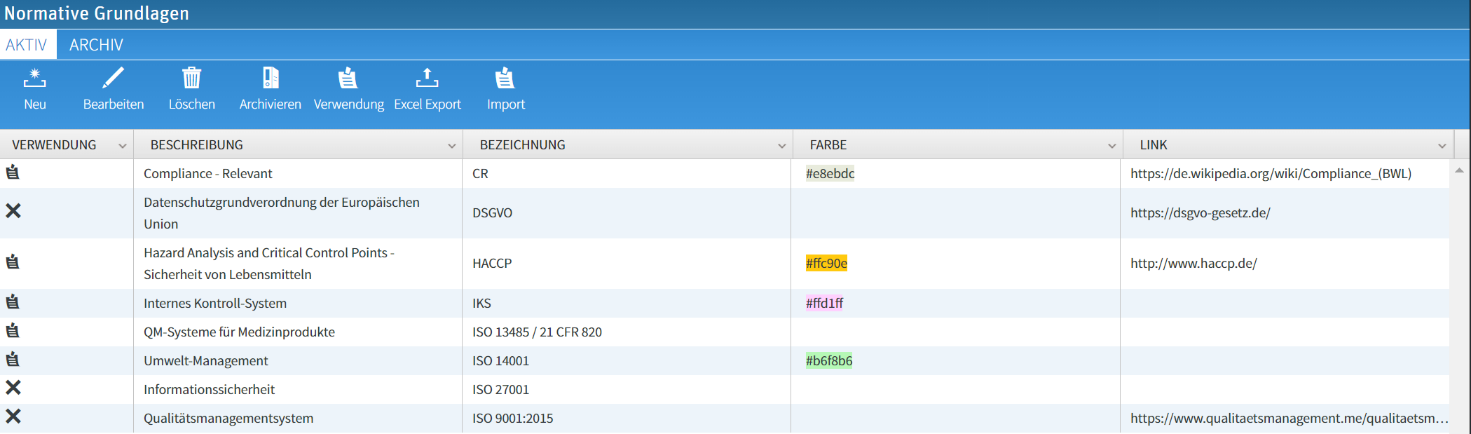
This table can be configured and extended as required. The usage of the entries can be displayed for all dependencies. This creates an overall picture of where (processes, documents, risks) a particular law/norm/directive is relevant to compliance.
Represent connections to processes, documents and risks
As can be seen in the Governance section using the example of process characteristics, the dependency between the normative basis and process/document/risk can be established by means of characteristic data fields. The data entered in the master data table is accessed via a selection list:
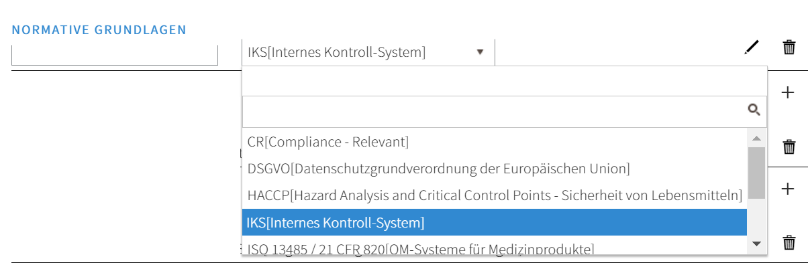
Each linked dependency can be evaluated and displayed via the usage display. Changes can be made centrally in the master data table. In the case of specific evaluations for individual standards/laws/guidelines, all compliance-relevant content can be displayed with a click.
Conclusion
The QM Pilot can be set up as a GRC tool. A holistic approach and structure of the system is ensured by database links and corresponding visual presentation in the user interface. As a standards-oriented system, functions such as versioning, testing and release workflow and ensuring access to exclusively released content are guaranteed. Extensive module descriptions can be found in the QM Pilot product brochure. This additional information only highlights certain aspects of the GRC system.

 ist ein Produkt der
ist ein Produkt der 